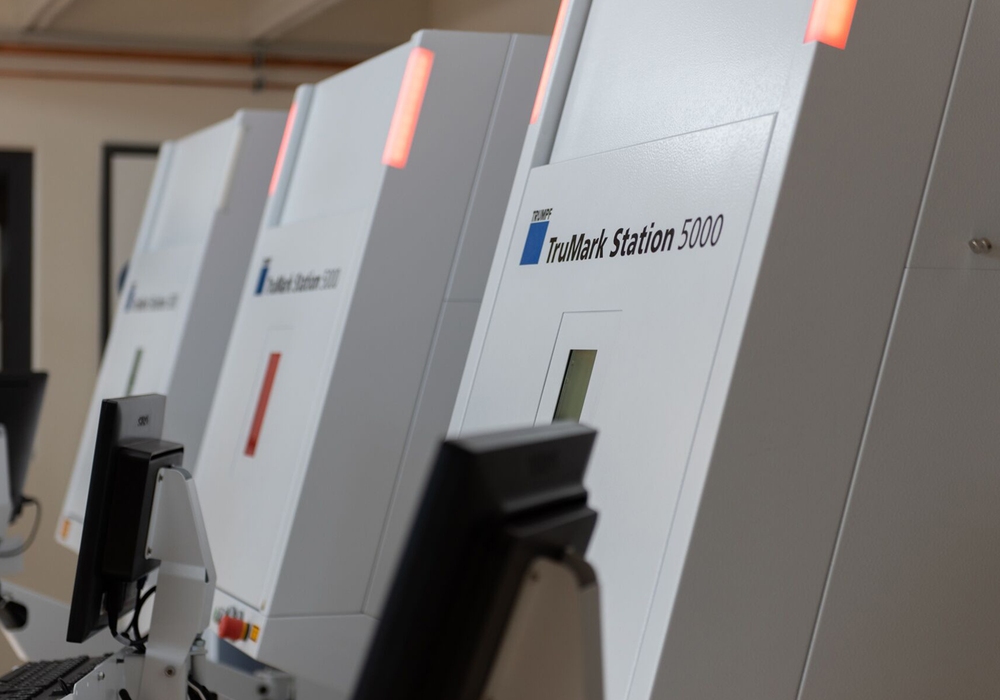
TRUMPF has a suite of TruMark Lasers that can be used to engrave or mark. The key differences between these two marking types are engraving removes material to create text or image whereas marking darkens, lightens or colours the surface, dependent on the material and laser source to create text or images such as Bar Codes, QR Codes and company logos. Discussions within this article hold true for both laser engraving and marking.
Laser marking can indeed offer several benefits for businesses involved in fabrication, including traceability and compliance. It provides advantages such as higher traceability, counterfeit protection, customisation capabilities, and the ability to create components that function as their own data carriers, which can be especially valuable in a smart factory environment. The contactless nature, flexibility, ease of integration, and high-quality results make laser marking a popular choice in manufacturing.
Laser Marking in sheet metal fabrication: Ensuring traceability and precision
In the realm of sheet metal fabrication, precision and traceability are paramount. Whether you’re manufacturing components for aerospace, automotive, Defence or various other industries, the ability to mark and track your products accurately is becoming essential with the introduction of programs such as I-Trace being trialed by the Australian Rail Associations in association with GS1. This is where laser marking technology stands out as a game-changer. This article will delve into the basics of laser marking, its importance in metal fabrication, and practical applications.
Understanding laser marking
Laser marking, also known as laser engraving or laser etching, is a process that uses a high-powered laser beam to create marks or patterns on the surface of a material. These marks can range from simple text and numbers to intricate logos and barcodes. Laser marking is distinguished by its ability to produce high-precision, durable, and visually appealing marks on a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, ceramics, glass, and more.
Traceability in laser marking
Traceability is a crucial aspect of many industries, particularly in healthcare, manufacturing, and aerospace. Laser marking plays a pivotal role in enhancing traceability by providing permanent and easily readable marks on products or components. Here’s how laser marking achieves this:
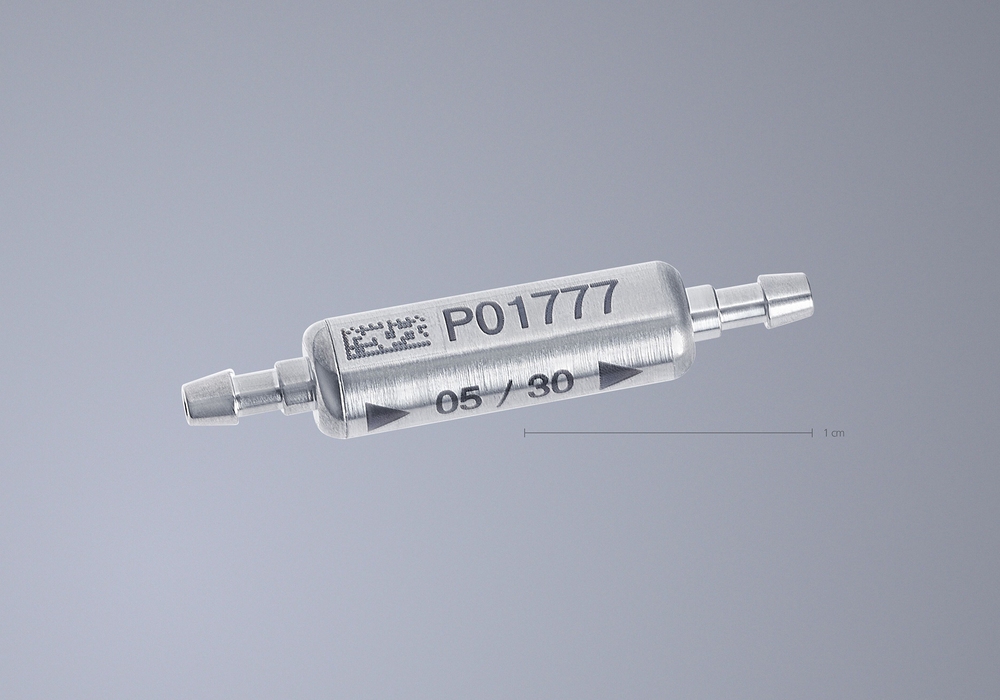
Data Matrix Codes: Laser marking can create high-density 2D Data Matrix codes that store essential information about a product, such as its manufacturing date, serial number, and batch number. These codes are compact yet contain a wealth of data, making them ideal for traceability.
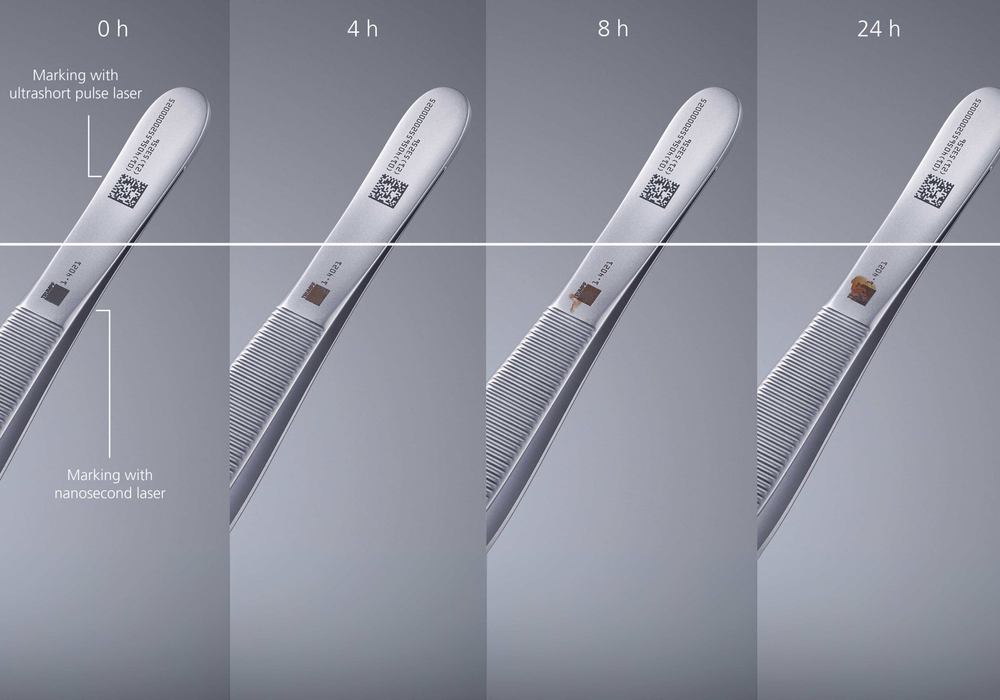
Consistency and durability: Laser marks are highly consistent and resistant to wear, corrosion, and environmental factors. This ensures that the traceability information remains intact throughout the product’s lifecycle.
High contrast: Laser marking creates high-contrast marks, making them easily readable by both humans and machine vision systems. This is essential for efficient traceability in automated manufacturing processes.
Practical marking applications
Laser marking finds extensive applications across various industries:
Medical Devices: Laser marks on medical instruments and implants enable precise tracking, ensuring patient safety and compliance with regulations.
Automotive: Laser marking is used for part serialisation, QR codes for maintenance information, and branding on automotive components.
Electronics: Circuit boards and electronic components are laser-marked for traceability and identification.
Aerospace: Laser marks on aerospace components provide crucial information for maintenance and quality control.
Jewellery: Precious metals and gemstones are marked with laser engravings for authentication.
In conclusion, laser marking stands out due to its exceptional traceability capabilities, precision, durability, and versatility. It plays a critical role in enhancing product identification, tracking, and quality control across a wide range of industries, making it an indispensable technology in today’s manufacturing landscape.
Laser marking stands out when compared with conventional marking methods due to quite a few advantages, which is why it has become a firmly established method within the industry.
The advantages briefly:
- High level of flexibility in the marking geometry
- High marking quality (very clear-cut edges)
- High reproducibility
- No tool wear due to non-contact processing (enables high quality at low costs)
- Low heat input affects material only minimally
- Easy integration into fully automatic production sequences
- No preparatory work or reworking is necessary
- Can be used on a wide range of materials (ceramics, metals, plastics, etc.)
- Very fine structures and small markings possible (into micron range)
- Option to mark large surfaces
- Can reach areas that are difficult to access
- High marking speed
- No expensive and potentially environmentally damaging disposable materials necessary, e.g. ink
- Indelible – no adhesive label that can be smudged or lost
- Rapid recognition and marketing via additional graphics or logos
Traceability
One of the reasons why manufacturing companies need to mark their products is that product liability laws and certifications have become stricter. This compels the industry to document which elements were processed and to assign them to each order and component accordingly. Manufacturers of security-related components in particular — such as suppliers for the automotive, defence sector, aerospace industries, medical technology and electronics/electrical engineering — are obliged to be able to report at any given time which of their individual components were used within complete systems. Only a permanent, easily readable marking can meet these requirements.
The requirements with which an industrial marking must often comply are:
- Permanent marking
- High contrast of the marking compared with the base material
- Machine readability (Including component and assembly level QR & bar codes)
- Material-conserving marking
- Integrated part marking into production documentation systems, for full traceabilityby documenting measurement or acceptance data directly on the component
Reasons why products should be marked to ensure traceability:
- Clear identification of components from incoming goods through to outgoing goods
- Identification of faulty components from particular batches, assisting ISO9001 compliance
- Documentation of statistical process and quality control
- Storage of working results and measuring data in one database
- Reading out and retrieval of processing programs (production control)
- Protection of original products against counterfeits
- Accurate factory material flow data for process improvement activities
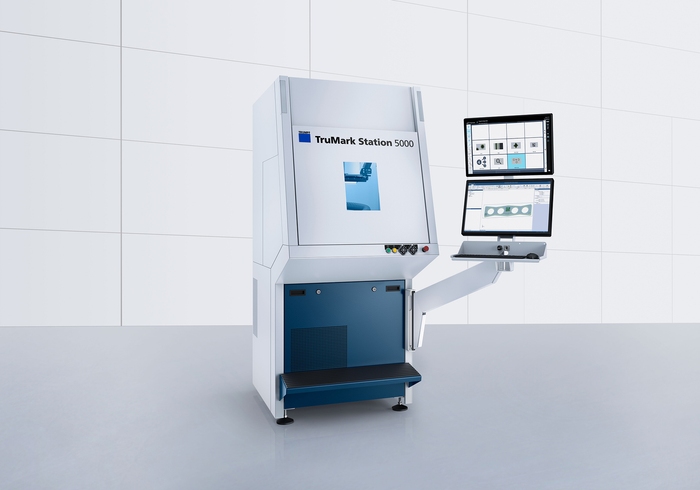
Fully integrated workstation for flexible all-around solution for convenient marking
Laser marking technology stands out in sheet metal fabrication and CNC machined parts due to its precision, durability, and the ability to facilitate traceability. In an industry where precision and accountability are crucial, laser marking ensures that metal products meet high standards of quality and compliance. As technology continues to advance, the role of laser marking in metal fabrication is likely to expand, further enhancing its importance in this field.
If your fabrication business is considering implementing laser marking for traceability and compliance purposes, it’s important to engage with specialists who can help you develop a customised solution tailored to your specific needs. Contact us today!